Lone working is increasingly prominent in the modern workplace, particularly in construction, healthcare, delivery services and security industries. Understanding the concept, risks and safety measures associated with lone working is essential for both employers and workers to ensure a safe and compliant work environment.
This guide will provide an in-depth look at the meaning of lone working, the associated risks and the best practices for managing these risks effectively.
What Does Lone Working Mean?
According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), lone working refers to workers carrying out their duties without close or direct supervision.
It’s currently estimated that there are seven to nine million lone workers in the UK alone, making up around 22% of the working population.
Who Is A Lone Worker?
There are lone workers in a wide range of job roles and settings, such as:
- Construction Workers: contractors, engineers and maintenance personnel who may work on-site or at individuals’ homes.
- Healthcare Professionals: nurses, doctors and social workers providing care in patients’ homes or community settings.
- Delivery Drivers: individuals who transport goods and services without direct supervision.
- Security Personnel: guards and watchmen working alone to monitor premises.
- Retail Workers: shop assistants in small stores who might work alone, particularly during early or late hours.
Lone Working Risks
Lone workers face unique risks compared to those who work in more conventional settings with nearby colleagues. Risks can include:
Workplace Hazards: some of the most common non-fatal injuries include slips, trips or falls, handling, lifting or carrying, being struck by a moving object, falls from height and acts of violence. Without someone nearby to help, these can quickly escalate into serious problems.
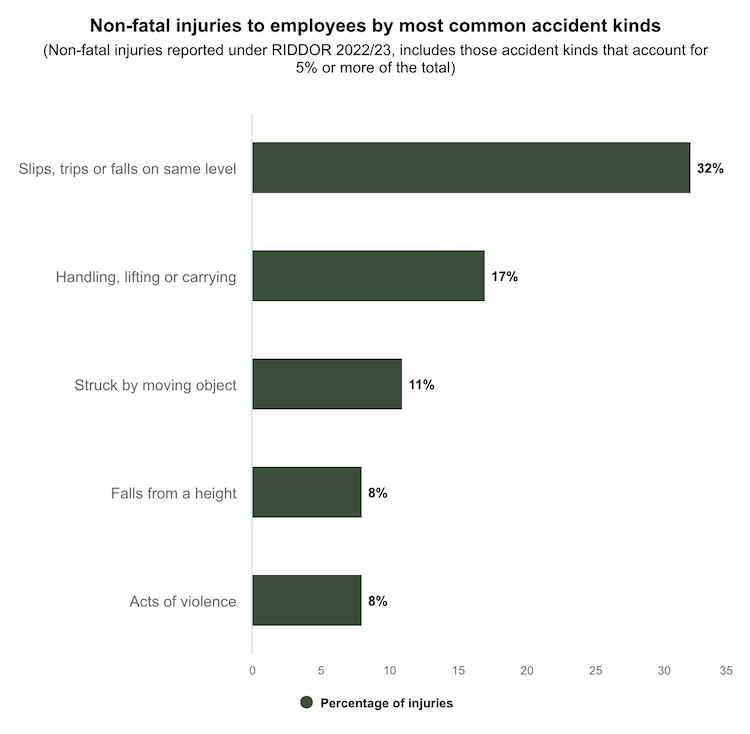
Source: HSE
- Violence And Harassment: over one in five people in employment experience some form of violence or harassment in the workplace, whether it’s physical, psychological or sexual. Lone workers are more vulnerable to physical or verbal abuse.
- Mental Health Issues: increased isolation can lead to stress, anxiety and other mental health challenges. In a report carried out by Skills for Care, it was found that mental health issues escalated quicker and remained unresolved for longer amongst lone workers as they were less visible to the rest of the workplace.
Related: Tackling Loneliness At Work
Legal And Regulatory Requirements
Understanding the legal and regulatory requirements for lone working is crucial for employers. In the UK, several regulations outline the responsibilities of employers regarding lone workers, including:
Health And Safety At Work Act 1974This act requires employers to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of all employees, including lone workers. |
Management Of Health And Safety At Work Regulations 1999These regulations mandate that employers conduct risk assessments and implement measures to mitigate identified risks. |
The Reporting Of Injuries, Diseases And Dangerous Occurrences Regulations (RIDDOR) 2013Employers must report certain incidents, injuries and dangerous occurrences involving lone workers. |
The Corporate Manslaughter And Corporate Homicide Act 2007This act holds organisations accountable for failures in health and safety management that result in fatalities. |
Employers must stay informed about these regulations and ensure compliance to avoid legal repercussions and ensure the safety of their lone workers.
Employer Responsibilities
Under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations, employers have a legal duty to manage the risks to lone workers. This includes:
Carry Out Lone Working Risk Assessments
A key component of managing lone working is carrying out a thorough risk assessment. The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 mandates that all employers must carry out general risk assessments. When assessing the risks for lone workers, consider the following steps:
- Identify Hazards: determine what could cause harm to lone workers in their specific roles.
- Evaluate Risks: assess the likelihood and severity of these hazards causing harm. If lone workers are operating at other workplaces, check the site-specific risks and ensure adequate control measures are in place.
- Implement Controls: put in place measures to eliminate or reduce the risks.
- Review And Update: regularly review the risk assessment to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
As an example, a lone worker on a construction site may face risks from operating heavy machinery or working at heights. In this case, the risk assessment would identify these hazards and implement controls such as safety training, regular equipment checks and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Get A Free Health Surveillance Template
Are you wondering whether you should adjust your Health Surveillance procedures for your project?
Enter your details to download our free Health Surveillance Template.
By submitting this form you confirm you are happy to be contacted by CHAS in accordance with our Privacy Policy
Training Programmes
Training is a critical part of managing the risks of lone working. Training programmes should cover the following:
- Risk Awareness: educate lone workers about the specific risks associated with their job roles.
- Safety Procedures: train workers on the safety procedures and protocols they need to follow
- Emergency Response: provide training on how to respond to emergencies, including first aid and incident reporting.
- Use Of Safety Equipment: ensure workers know how to use any safety equipment provided, such as personal alarms or communication devices.
Develop A Lone Worker Policy
A well-structured lone-working policy is essential for managing risks effectively. This policy should clearly define:
- Scope And Objectives: Outline who the policy applies to and its main goals.
- Roles And Responsibilities: Specify the responsibilities of employers, managers and lone workers.
- Procedures And Protocols: Detail the procedures for conducting lone working risk assessments, reporting incidents and maintaining communication.
- Emergency Procedures: Provide clear guidelines on what to do in case of an emergency.
- Review And Monitoring: Describe how the policy will be monitored and reviewed to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
An effective lone-working policy helps create a safe working environment by providing clear guidelines and expectations for both employers and employees.
Make Use Of Technology And Tools
With the advancement of technology, there are now many tools available to help safeguard lone workers and reduce risks. Some solutions you could consider include:
- Personal Alarms: devices that lone workers can carry to alert others in case of an emergency.
- GPS Trackers: these could be mobile apps or external devices that allow employers to monitor the location of lone workers in real time.
- Wearable Technology: certain smart devices can monitor vital signs and detect falls or other emergencies.
- Regular Check-Ins: establish check-in procedures where lone workers must report their status at certain times, such as arrival and departure of locations.
- Buddy Systems: pair lone workers with a buddy that can be contacted in the event of an emergency.
Lone Worker Responsibilities
Lone workers play a crucial role in maintaining their own safety and that of others who may be affected by their work. To ensure a safe working environment, lone workers should adhere to the following responsibilities:
Take Care Of Their Own Health And Safety
Lone workers must be vigilant about their own health and safety. This includes being aware of their surroundings, recognising potential hazards and taking proactive steps to mitigate risks. They should follow safe work practices and avoid taking unnecessary risks.
Safeguard The Health And Safety Of Others
It’s important for lone workers to be mindful of how their actions might impact others. They should ensure that their work does not pose a risk to the safety of colleagues, clients, or the public.
Abide By Employers’ Health And Safety Procedures
Lone workers must follow all health and safety policies and procedures established by their employer. This includes adhering to guidelines on safe work practices, emergency procedures and reporting protocols.
Use Tools And Equipment Properly
Proper use of tools and equipment is essential for preventing accidents. Lone workers should ensure they are trained in the correct use of any tools or machinery they are required to operate and should always use them according to the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines.
Report All Accidents And Injuries
Prompt reporting of all accidents, injuries and near misses is vital for maintaining workplace safety. Lone workers should immediately inform their employer or supervisor of any incidents, regardless of how minor they may seem. This helps address hazards promptly and may prevent future incidents.
By carrying out these responsibilities, lone workers contribute to creating a safer and more secure working environment for themselves and others.
Lone working presents unique challenges and risks that require careful management and proactive measures. By understanding the nature of lone working, conducting thorough risk assessments and implementing effective policies and procedures, employers can ensure a safer and more supportive environment for lone workers.
Take the first step towards improving your company’s safety standards by joining Veriforce CHAS today. Access top-tier contractors and comprehensive risk management tools from a leader in compliance and safety.
Get A Free Occupational Health Policy
Are you wondering whether you should update your Occupational Health Policy?
Enter your details to download our free Occupational Health Policy.
By submitting this form you confirm you are happy to be contacted by CHAS in accordance with our Privacy Policy