Examining the profound impact of energy on the environment, we shed light on the crucial balance between meeting our energy demands and preserving the natural world.
In today’s interconnected world, the intersection of energy production and environmental conservation is increasingly critical. Energy production, primarily through fossil fuels, is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, notably CO2. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that the energy sector accounts for a staggering three-quarters of total global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This is hardly surprising — 80% of the world’s energy supply comes from fossil fuels, with oil making up 30%, followed by coal (27%) and natural gas (24%).
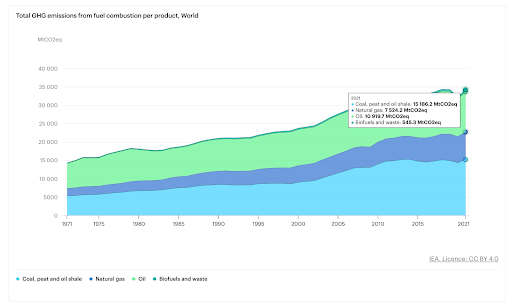
Source: IEA
While the environmental challenges of energy production are significant, they are not insurmountable. The transition to sustainable energy sources and efficient practices can balance our energy needs with environmental conservation, ensuring a sustainable future.
From the air we breathe to the water we depend on, energy production leaves an indelible mark on our natural world. Here, we explore not only the challenges but also the opportunities for balancing our energy needs with environmental stewardship.
Related Reading: Proactive Risk Management For Utilities: Why Does It Matter?
Understanding The Impact Of Energy On Environment
Energy production, a cornerstone of modern civilisation, comes with significant environmental consequences. The key lies in recognising and managing these impacts, from air pollution to land usage.
The most visible and debated of these is the emission of CO2, a byproduct of burning fossil fuels. Notably, coal and oil are major contributors, with coal accounting for around 40% of these emissions. The various environmental repercussions of energy production emphasise the need for efficient management and sustainability.
But there’s a complex interplay between energy generation, air and water pollution, solid waste management, and land use. Understanding these challenges is crucial in mitigating the impact of energy on the environment.
- Air pollution, predominantly caused by the burning of fossil fuels, leads to a range of environmental challenges. CO2 emissions, a primary concern, are closely linked to global warming and climate change. Beyond CO2, other emissions such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides contribute to issues like acid rain and ozone layer depletion, further exacerbating environmental harm.
- Solid and liquid waste management presents another facet of this complex issue. The energy sector, particularly the coal and oil industries, is responsible for significant waste that needs careful handling to avoid further environmental degradation. Effective management of this waste is crucial in mitigating its impact on both land and water ecosystems.
- Land use for energy production, especially in renewable energy sectors like wind, solar, and hydro, requires extensive areas, leading to a trade-off between energy generation and land conservation. Each of these aspects demonstrates the intricate balance required to effectively manage energy production’s environmental impact, a balance at the core of promoting sustainable and responsible energy practices.
Related Reading: Proactive Risk Management For Utilities: Why Does It Matter?
Emissions And Their Global Impact
The global impact of emissions from energy production is a critical concern, especially considering the vast quantities of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. For example, in 2019, the total greenhouse gas emissions in the UK were over 550 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (Mt CO2e).
This marked a decrease of approximately 3% from the previous year, continuing the downward trend in greenhouse gas emissions in the UK since 1990. The primary contributors to these emissions remain households and the energy, manufacturing, and transport sectors, accounting for over 72% of the total emissions.
CO2 emissions, primarily from the combustion of fossil fuels like coal and oil, are central to discussions about climate change. These emissions have a far-reaching impact on global warming, influencing weather patterns and ecological systems worldwide.
Apart from CO2, other emissions such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides contribute to environmental issues like acid rain and the depletion of the ozone layer. These pollutants, largely emitted from coal and oil combustion, pose significant health risks and ecological challenges. Addressing these emissions is not just a local issue but a global imperative.
This global challenge of managing gaseous emissions is yet to be effectively addressed. While efforts are in place, the international community’s response requires further strengthening. As we explore these environmental impacts, it’s clear that a concerted, global effort is needed to manage and mitigate these emissions.
Navigating New Horizons: Recent UK Legislation On Energy And Environment

The United Kingdom is charting a bold course towards a sustainable energy future, marked by two significant legislative milestones: the reforms to the UK Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) and the introduction of the Energy Act 2023.
- UK Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) Reforms (2024): As of 2024, the UK will implement tighter emission limits for the power sector, energy-intensive industries, and aviation. This move, part of the ETS reforms announced in July 2023, is a strategic push to reduce the carbon footprint across these sectors.
- The scheme, which has been in effect since 2021, incentivises the reduction of emissions through investments in energy efficiency and cleaner, renewable technologies. These reforms also expand the ETS to cover additional sectors such as domestic maritime transport and waste, aligning with the UK’s ambitious climate goals.
Related Reading: Five Steps To Improve Energy Efficiency
- The Energy Act 2023: Enacted in October 2023, this groundbreaking legislation aims to overhaul the UK’s energy system. Its focus is threefold: bolstering energy security, advancing the net zero agenda, and ensuring long-term affordability of energy bills.
- The Energy Act 2023 introduces a range of measures, from fostering competition in electricity networks to new frameworks for Energy Smart Appliances. The Act also extends the regulatory authority of Ofgem to heat networks and sets forth new consumer protections, promoting investments in low-carbon solutions like heat pumps and smart metres.
Related Reading: Government Drives Towards A Net-Zero Carbon Future
These legislative advancements reflect the UK’s commitment to reducing the environmental impact of energy on the environment. By blending regulatory reform, market-based incentives, and technological innovation, these laws pave the way for a greener, more sustainable energy landscape.
Addressing Solid And Liquid Waste Management
The management of solid and liquid waste in the energy sector is a critical aspect of minimising its environmental impact. Coal mining, for instance, generates significant amounts of waste, including coal ash, which must be carefully managed to prevent environmental contamination. The handling and disposal of this waste are crucial in protecting both land and water ecosystems.
Similarly, the oil industry faces challenges with oil spills, which have far-reaching environmental impacts. While large-scale spills are relatively rare, their consequences can be devastating, affecting marine life and coastal ecosystems. Effective measures and contingency plans are essential in preventing and mitigating such incidents.
Nuclear energy production also results in waste, notably in the form of spent nuclear fuel. The management of this waste is a delicate matter, requiring secure and long-term solutions to prevent environmental contamination.
These challenges highlight the importance of comprehensive waste management strategies in the energy sector. Effective waste management is integral to reducing the impact of energy on the environment, aligning with global efforts towards more sustainable energy practices.
The Growing Concern Of Water Use In Energy Production
Water use in the energy sector is becoming an increasingly critical issue. The process of unconventional oil and gas production, along with the cooling requirements of power plants, demands significant amounts of water.
Even renewable energy sources like concentrating solar plants have substantial water needs. Although the energy sector’s water usage is relatively small compared to agriculture and industry, the competition for this vital resource is intensifying.
This growing concern over water use in energy production highlights the need for effective water management strategies. It is essential to work towards minimising water consumption and improving recycling methods in the energy sector. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also prepares for future challenges in resource availability.
Land Use And Renewable Energies
The impact of energy on the environment is significantly influenced by land use, particularly in the case of renewable energy sources like wind, solar, hydro, and biofuels. These sources, while sustainable, require larger land areas compared to more concentrated energy sources like nuclear and fossil fuels. This brings into focus the societal and environmental trade-offs in energy production.
Decisions about land use for energy production are complex and must consider factors like ecological impact, land availability, and specific energy requirements. The challenge lies in balancing the need for renewable energy with the conservation of land resources. This approach is crucial in minimising the environmental impact of energy while catering to the growing global energy demand.
Balancing Environmental Impact With Affordability
Balancing the environmental impact of energy production with the cost is a crucial aspect of sustainable development. Making energy production less impactful often comes at a higher cost, which is eventually borne by consumers. As energy prices continue to rise, finding a way to minimise environmental impact while keeping energy affordable becomes a pivotal challenge.
This balance is essential for maintaining the economic growth and prosperity that affordable energy brings, which in turn facilitates further investment in environmental sustainability. Compliance and risk management become instrumental in achieving this balance, ensuring that the impact of energy on the environment is managed effectively without compromising on affordability.
Take The First Steps Towards Sustainability With Veriforce CHAS
A sustainable future in energy production requires a fine balance, not only in maintaining industry profitability but also in minimising environmental impacts. With the introduction of our new CHAS Social Sustainability verification, we’re elevating our commitment to sustainability.
This innovative tool empowers you to scrutinise and manage your supply chain’s sustainability performance across 17 critical topics, covering emissions, energy management, water consumption, and pollution monitoring, among others.
Veriforce CHAS is your partner in seamlessly integrating sustainability into your operations by connecting you with a network of contractors who adhere to stringent sustainability regulations and best practices, paving the way towards achieving net zero.
Become a CHAS Client today to join the global movement of building a more sustainable energy sector. Reach out to our award-winning team at 0345 521 9111 to get started.
Are You Ready To Be A CHAS Client?
Sign up for FREE today or learn more about our client services by scheduling a callback with one of our friendly CHAS advisors.